Your participation in the two surveys below, aimed to gather your insights and perspectives on accessibility and accommodations at colleges and universities, is greatly valued and appreciated.
TIPS Pre-course survey
Evaluation Survey
Welcome students, parents, teachers and support professionals. We’re excited to have you here!
Welcome to Transition into Post-Secondary Studies (TIPS). If you’re a high school student, it means you’re probably considering making one of the biggest decisions of your life: to attend college or university! You may also be an adult student who is making your way through your post-secondary studies. For either situation, this course was designed to guide you through the planning required and to provide you with the information, knowledge, and skills that will help you confidently manage your journey in post-secondary education, campus life, your practicum experiences, and beyond.
Developed by ACE-BC’s team, this online course is as an extension of workshops that were created in collaboration with the Canadian Hard of Hearing Association – BC Chapter’s Youth Peer Support Program, an audiology consultant, The Provincial Deaf and Hard of Hearing Services, The Deaf, Hard of Hearing, Deaf-Blind Well-Being Program, along with additional support from Assistive Technology-BC (ATBC) and the Inclusive Campus’ DREAM project which supports students in their classroom and practicum experiences.
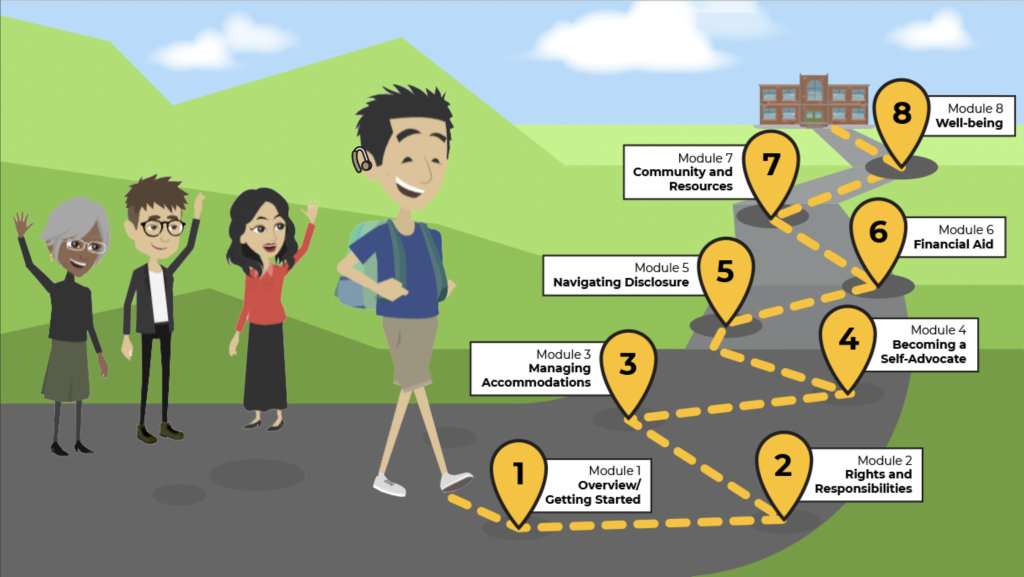
We hope this course helps you create your action plan as you start or continue your post-secondary education. We also invite you to register for our Student Mentorship Program for extra support support as you navigate this journey.
This course is designed for students who are Deaf, hard of hearing, Deaf-Blind/deafblind, or have additional disabilities. We understand that transitioning to post-secondary education can be a big step for all students. Many of the skills you’ll learn, like self-advocacy and disclosure, apply to anyone needing support to access the learning environment. Our goal is to make this transition easier for you and your support network.
We also believe that access and inclusion are shared responsibilities within the post-secondary system. ACE-BC also provides support and resources to the post-secondary institutions, to help improve accessibility in all facets of the learning environments.
We look forward to supporting your success in your educational studies!
If you have any questions or feedback about this course, you can leave a video or chat message on our website, or email us at: office@ace-bc. Please be sure to complete the pre and post-surveys. Your feedback will help us ensure that our content is as valuable and relevant as possible for you.
